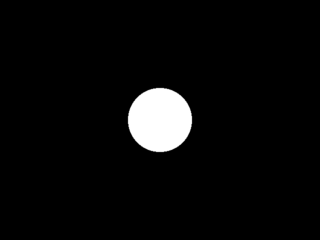
5 points
pixel trace
Bare minimum to getting started: flat shading, sphere intersections, casting rays.
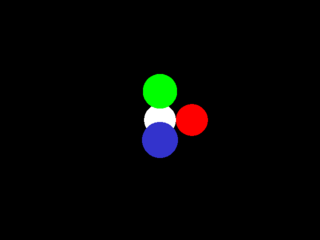
5 points
Get the coordinate system oriented correctly, introduce colors.
1 points
Test image size and camera settings.
1 points
pixel trace
Test irregular camera orientation.
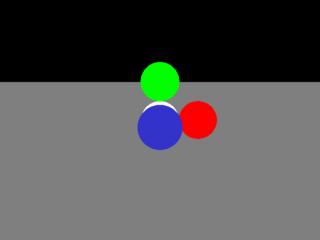
3 points
Get basic plane intersections working.

3 points
pixel trace
Add Phong shading (diffuse only) and handle point lights.

1 points
pixel trace
Phong shading with sphere - diffuse only.

1 points
Phong shading colored material and colored light. Diffuse only.

1 points
pixel trace
Add specular.
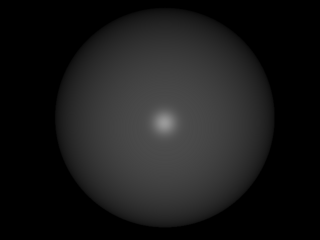
1 points
pixel trace
Both diffuse and specular.
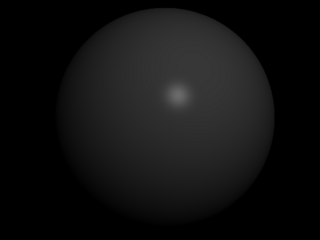
1 points
pixel trace
Move light off center; break symmetry.
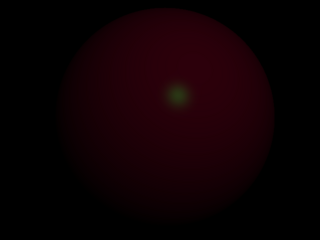
1 points
Colors with lights, diffuse, and specular.
1 points
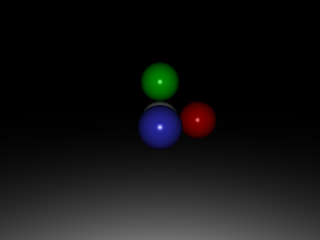
Phong shading with full scene.
1 points
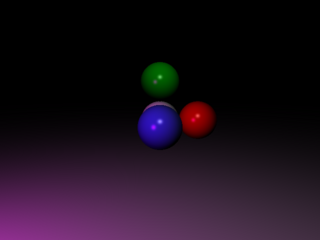
Add color to the lights; make sure things work with two lights.

1 points
Add background shader, introduce ambient light.

1 points
Shading test.

1 points
Specular shading test - test exponent.

1 points
Specular shading test - test exponent.

1 points
Specular shading test - test exponent.

1 points
Specular shading test - test exponent.
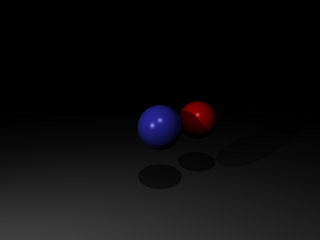
2 points
pixel trace
Introduce basic shadows. This is also a bug test; there is a very bright light hidden under the ground.

1 points
Bug test: objects behind the light.

1 points
Bug test: object covering up the light. Since no light escapes, the image should only contain ambient light.
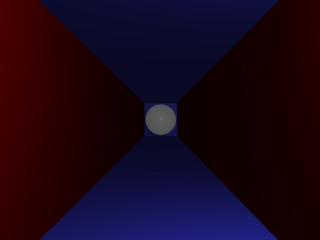
1 points
pixel trace
Test recursion depth.
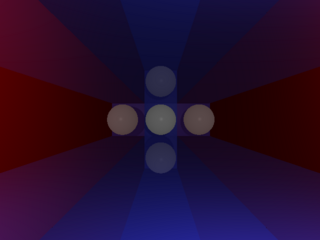
1 points
Test recursion depth.

1 points
pixel trace
Test recursion depth.
1 points
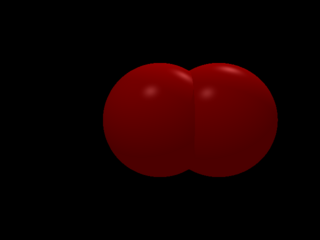
pixel trace
Start implementing Booleans: basic union.
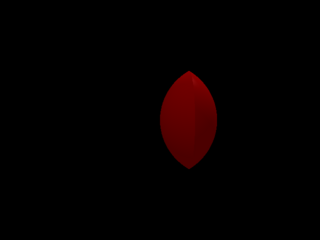
1 points
Start implementing Booleans: basic intersection.
1 points
pixel trace
Start implementing Booleans: basic difference. Check to make sure that complex objects can cast shadows on themselves.
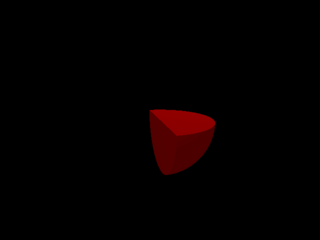
1 points
Handle nesting of Booleans.

1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: check complex interaction of Booleans.
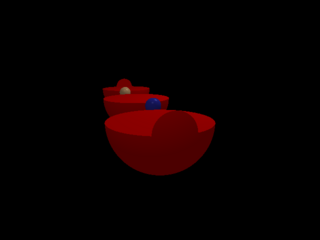
1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: check complex interaction of Booleans.
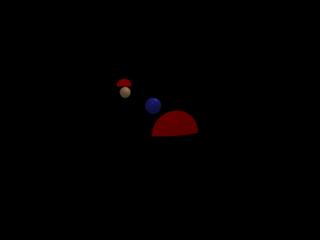
1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: check complex interaction of Booleans.

1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: check complex interaction of Booleans.
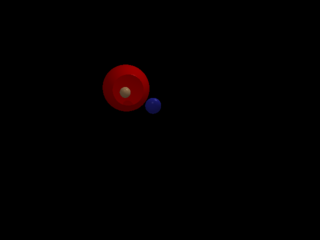
1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: check complex interaction of Booleans.
1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: make sure degenerate cases are handled correctly. Union and intersection with duplicate objects is easy to deal with and should would correctly. Note that the difference of duplicate objects is somewhat ambiguous, so this case is not tested.
1 points
Construct a bounded object from unbounded primitives.
1 points
pixel trace
Complex Booleans and self-shadowing.

1 points
pixel trace
Bug test: what happens if we construct a hollow piece of geometry and fill it with a camera, lights, and objects?
1 points
pixel trace
Start implementing transforms. Translation only.
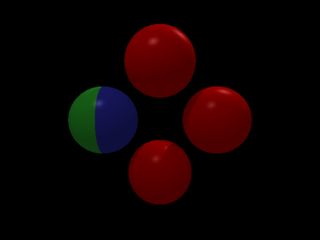
1 points
pixel trace
Start implementing transforms. Rotation only.
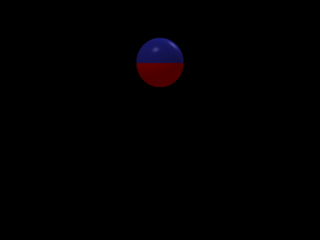
1 points
pixel trace
Start implementing transforms. Scale only.
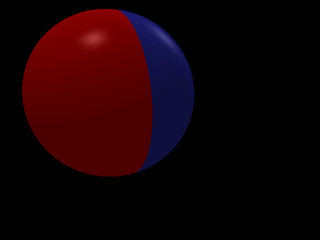
1 points
pixel trace
Make sure transforms can be combined correctly. Note that exactly the same transformation is being applied in two ways: as a series of separate transforms and combined within a single transform.

1 points
pixel trace
Make sure transforms work correctly with booleans.

1 points
pixel trace
Start implementing torus
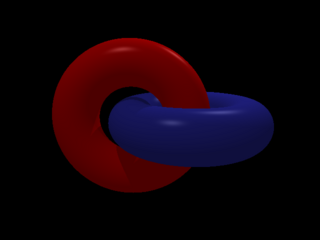
1 points
pixel trace
Make sure all of the parameters to torus work.
1 points
pixel trace
Make sure torus works with booleans. This is also a bug test; the camera is inside the torus, but it is outside of the visible boolean object.